Since its inception in 1958, NASA has not only been at the forefront of space exploration but also a master of capturing the public imagination. The agency understood early on that space missions needed more than scientific success—they required public interest, political support, and a sense of wonder. By blending cutting-edge technology, daring exploration, and a carefully crafted narrative of glamour and heroism, NASA transformed space travel from a niche scientific endeavor into a global cultural phenomenon.
This article explores how NASA sold the science and glamour of space travel, examining its strategies, milestones, and enduring impact on public perception, education, and science communication.
The Early Days: Sputnik, the Space Race, and Public Attention
The launch of Sputnik 1 by the Soviet Union in 1957 shocked the United States, triggering the space race. NASA’s establishment in 1958 was as much about technological and scientific leadership as it was about winning hearts and minds.
Early NASA strategies included:
-
Dramatic launches and media coverage: Rocket launches were designed to awe the public.
-
Astronaut heroism: Early astronauts like Alan Shepard and John Glenn were portrayed as national heroes.
-
Education campaigns: Schools and universities were encouraged to promote STEM education in the context of space exploration.
By connecting space achievements to national pride and human adventure, NASA generated public enthusiasm that fueled funding and political support.
Apollo Program: Glamour Meets Science
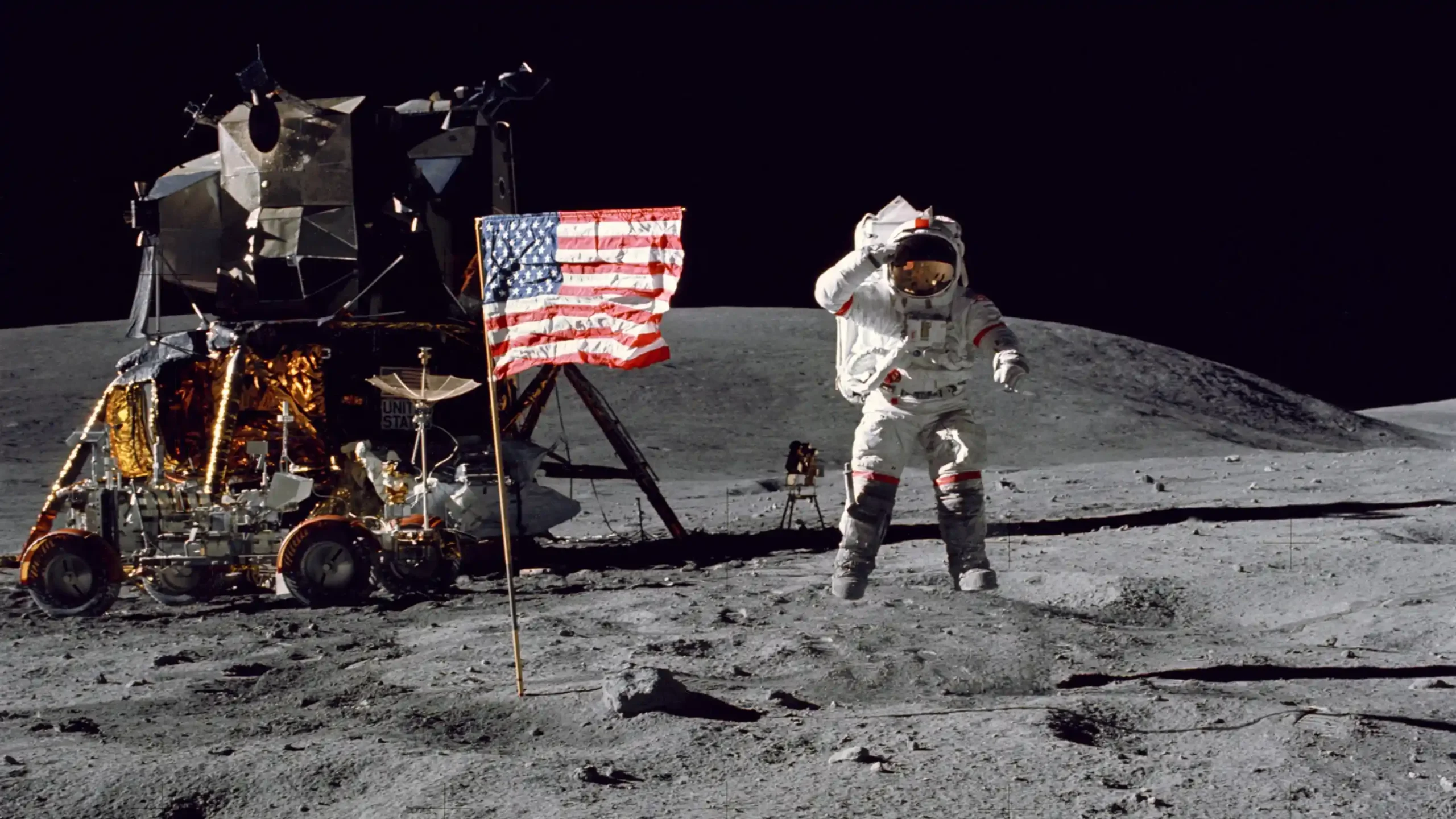
The Apollo program is NASA’s most iconic example of selling space travel. Apollo missions combined scientific achievement with highly visual and emotional storytelling.
1. Moon Landings as Spectacle
-
The 1969 Apollo 11 moon landing was broadcast live to millions worldwide.
-
Images of astronauts planting the American flag created a powerful, aspirational narrative.
-
The juxtaposition of human courage and technological sophistication highlighted the glamour of space exploration.
2. Scientific Communication
-
Lunar rock samples and geological data were shared with the global scientific community.
-
NASA ensured that the public understood why moon rocks mattered, linking exploration to knowledge creation.
-
The agency balanced technical data with visually compelling imagery, making science accessible and exciting.
3. Astronaut Branding
-
Astronauts became cultural icons.
-
Public appearances, speeches, and educational outreach emphasized their bravery, intelligence, and humanity.
-
This approach personalized space travel, giving it a relatable, glamorous face.
Satellites and Robotic Missions: Glamour Beyond Human Presence
NASA’s promotion of space missions extended beyond human astronauts. Robotic missions captured public attention through stunning visuals and narratives of discovery:
-
Hubble Space Telescope: Released breathtaking images of galaxies, nebulae, and cosmic phenomena.
-
Mars Rovers (Spirit, Opportunity, Curiosity, Perseverance): Public engagement soared with images of Martian landscapes and rover “selfies.”
-
Voyager Missions: Iconic images of Jupiter, Saturn, and deep space communicated the grandeur of the cosmos.
By highlighting the visual beauty of space, NASA sold the glamour of exploration even without humans on board.
Media Strategy: Making Science Accessible
NASA recognized early that public understanding drives support. The agency deployed several media strategies:
1. Television and Live Broadcasts
-
Launches, landings, and spacewalks were broadcast live, turning events into shared global experiences.
-
Commentary explained complex science in simple, engaging terms, making missions accessible to all ages.
2. Photography and Film
-
High-resolution images, films, and documentaries were produced for public consumption.
-
NASA partnered with filmmakers and photographers to create narratives that emphasize wonder and achievement.
3. Social Media and Digital Engagement
-
Modern NASA engages millions through Twitter, Instagram, YouTube, and TikTok.
-
Posts highlight both scientific discoveries and human stories, keeping space exploration in public discourse.
By controlling how information was presented, NASA ensured that space exploration remained aspirational and glamorous.
Educational Outreach: Inspiring the Next Generation
NASA’s emphasis on public engagement extended into education:
-
STEM programs: NASA provided lesson plans, workshops, and competitions to inspire students.
-
Interactive content: Apps, virtual reality experiences, and online simulators allowed users to experience missions virtually.
-
Public lectures and exhibitions: NASA centers hosted tours, presentations, and interactive displays.
This approach framed space exploration as a glamorous career path, encouraging young people to pursue science, engineering, and space-related professions.
Balancing Glamour and Science
While NASA’s media efforts emphasized the excitement and heroism of space, the agency also maintained credibility by highlighting scientific rigor:
-
Press releases included data summaries alongside visuals.
-
Scientists and engineers were given public platforms to explain their work.
-
Publications and research papers ensured that discoveries reached academic and professional audiences.
This balance ensured that space exploration was both inspiring and credible, blending glamour with substance.
NASA Branding and Public Image
NASA’s iconic branding, including the “meatball” logo and the worm logotype, reinforced the agency’s identity. These symbols were:
-
Featured on spacecraft, satellites, and astronaut uniforms
-
Widely recognized in popular culture
-
Used in merchandise, posters, and educational materials
The branding emphasized technological sophistication and national pride, creating an aspirational image of the agency and its missions.
Cultural Impact of NASA’s Glamour Strategy
NASA’s approach shaped not only public perception but also culture:
-
Science fiction influence: Movies and books drew inspiration from NASA missions, creating a feedback loop of interest in space.
-
Public fascination: Citizen interest in astronomy, space science, and STEM careers grew significantly.
-
Global inspiration: NASA’s missions inspired audiences worldwide, demonstrating that space exploration transcends borders.
The glamour of space travel became a tool for engaging society with science.
Modern Era: Artemis and Commercial Partnerships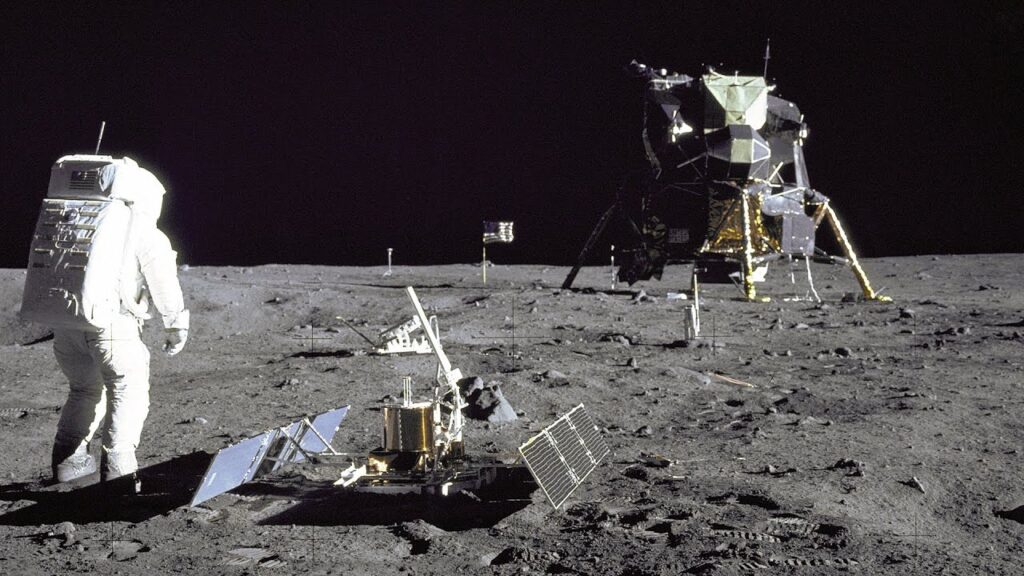
In the 21st century, NASA continues to sell space travel as glamorous while advancing scientific goals:
-
Artemis program: Promises a return to the Moon with astronauts of diverse backgrounds.
-
Commercial partnerships: Collaborations with SpaceX, Blue Origin, and other private companies enhance visibility and excitement.
-
Public engagement campaigns: High-quality videos, livestreams, and interactive websites showcase missions in real time.
Modern missions combine cutting-edge science with visual storytelling, ensuring continued public enthusiasm.
Science and Technology as Entertainment
NASA recognized that people connect with storytelling. The agency leveraged:
-
Visual media: Stunning images from Hubble, Mars rovers, and Earth-observing satellites.
-
Human stories: Profiles of astronauts, engineers, and scientists.
-
Narratives of discovery: Framing missions as adventurous journeys into the unknown.
By combining science with entertainment, NASA made exploration accessible, aspirational, and glamorous.
Lessons from NASA’s Approach
NASA’s success in selling space travel provides several lessons:
-
Narrative Matters: Science is more compelling when told as a story of human adventure.
-
Visuals Inspire: High-quality images and videos create awe and curiosity.
-
Accessibility is Key: Explaining complex science in relatable terms increases engagement.
-
Human Element Enhances Connection: Showcasing people behind the missions personalizes science.
-
Continuous Innovation: NASA adapts media strategies to new platforms and technologies.
These principles are applicable to science communication, public engagement, and education across disciplines.
Conclusion
NASA’s ability to sell the science and glamour of space travel has been a critical component of its success. By combining breathtaking imagery, compelling narratives, and rigorous scientific achievement, NASA captured the world’s imagination and created a lasting legacy of public support. From the Apollo moon landings to the Mars 2020 mission, the agency has shown that space exploration is not only about data and discovery but also about inspiring wonder and aspiration.
Today, as NASA ventures toward the Moon, Mars, and beyond, the agency continues to blend science with spectacle, ensuring that space travel remains both credible and captivating. In doing so, NASA proves that the universe is not only a subject of study but also a canvas for human imagination, ambition, and inspiration.
Read Also: Keep your face towards the sunshine and shadows will fall behind you
Watch Also: https://www.youtube.com/@TravelsofTheWorld24












Leave a Reply