NASA is entering a new era of transformation, and the message from its leadership is clear: change is not coming—it is already happening. The Acting NASA Administrator has announced a new wave of “shakeups”, signaling the agency’s intention to reform internal structures, accelerate mission timelines, and strengthen partnerships with the commercial space sector. These changes come at a critical time when global competition in space is rising, budgets are tightening, and the United States is preparing for some of the most ambitious missions in NASA’s history.
From lunar exploration under the Artemis program to deeper collaboration with private companies, the acting chief’s announcement underscores a pivotal shift. The goal is to make NASA faster, more adaptive, and better aligned with modern space challenges. These shakeups are not just administrative—they represent a strategic overhaul aimed at protecting NASA’s leadership in space for decades ahead.
Why NASA Is Pushing for Major Internal Shakeups
NASA’s current landscape is defined by intense global competition. Countries like China, India, and members of the European Union have increasingly ambitious space agendas. Private companies—especially SpaceX, Blue Origin, and other emerging space enterprises—are innovating faster and cheaper than ever before. Meanwhile, NASA is preparing for historic missions, including the return of astronauts to the Moon through Artemis, the development of new Mars exploration systems, and the expansion of space-based science.
In this context, the acting administrator has emphasized that NASA cannot rely on old structures, slow processes, or outdated management systems. To maintain leadership, the agency must modernize.
The new shakeups, as outlined, aim to:
-
Streamline mission approval and review processes
-
Improve coordination between NASA centers
-
Increase accountability and project transparency
-
Strengthen industry partnerships
-
Enhance NASA’s ability to deliver missions on time and within budget
These reforms are not optional—they’re essential for NASA to meet its goals in the coming decade.
A Focus on Artemis: Fixing Delays and Structural Challenges
One of the key motivators behind the shakeups is NASA’s Artemis program. Designed to return humans to the Moon and establish a sustainable presence there, Artemis has faced delays, budget overruns, and logistical challenges.
The acting chief acknowledged these issues directly, noting that certain structural inefficiencies must be addressed for Artemis to succeed. Some projects have taken too long to transition from concept to production. Others have lacked clear oversight. Partnerships with commercial contractors—though essential—have sometimes struggled due to unclear expectations or shifting program demands.
The shakeup will prioritize:
-
Faster decision-making on hardware changes
-
Improved integration between NASA centers and contractors
-
Establishing realistic schedules to avoid constant delays
-
Implementing more frequent review cycles to ensure progress
-
Strengthening the Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate
NASA’s leadership believes that once these adjustments take effect, Artemis missions will run more smoothly, more efficiently, and more predictably.
Strengthening NASA’s Commercial Partnerships
One of the most significant areas the acting chief focused on is NASA’s partnership with the commercial space sector. Over the past decade, private companies have played a transformative role in spaceflight. SpaceX, in particular, has revolutionized launch costs and spacecraft development timelines. United Launch Alliance, Blue Origin, Rocket Lab, and others are increasingly important players in NASA missions.
However, the acting administrator pointed out areas where NASA must improve its collaboration model. These include:
-
Faster contracting
-
More flexible agreements
-
Better-defined expectations
-
A clearer balance between competition and cooperation
The shakeups will include a stronger Commercial Operations Program Office, focused on integrating private companies into NASA’s long-term strategy for space transportation, lunar landers, and orbital infrastructure.
NASA sees the commercial sector not as a rival but as a critical partner for future missions. The shakeups aim to ensure that NASA can keep up with the agility of the private sector while maintaining its scientific and safety standards.
Restructuring NASA Centers: A Modern Approach
Another major component of the shakeups involves changes within NASA’s internal organizational structure. With 10 major centers across the United States, NASA has historically faced challenges in coordinating tasks across multiple states, teams, and specialties.
The acting chief stated that some centers need updated roles, while others may require shifts in leadership or mission priorities. This does not necessarily mean downsizing—rather, NASA wants to clarify center responsibilities so that efforts are not duplicated or misaligned.
Potential changes include:
-
New leadership rotations
-
Reassignments of center responsibilities
-
Updated mission roles for key facilities
-
Stronger communication channels between centers
The goal is to create a more unified and efficient NASA, where each center’s strengths are fully utilized.
A New Emphasis on Workforce Development
Behind NASA’s spacecraft, telescopes, and missions is one of the most skilled workforces in the world. Yet the acting administrator highlighted concerns that NASA must evolve its workforce to meet modern space demands. Many of NASA’s employees are approaching retirement age, and recruitment for highly specialized fields—like advanced robotics, AI engineering, plasma physics, and cybersecurity—has becoming increasingly competitive.
As part of the shakeups, NASA plans to:
-
Expand internship and fellowship opportunities
-
Strengthen partnerships with universities
-
Recruit more aggressively in STEM fields
-
Invest in training programs for current employees
-
Restructure teams to increase cross-disciplinary collaboration
These changes ensure that NASA will continue to attract top talent and maintain its scientific excellence.
Better Oversight of Major Space Missions
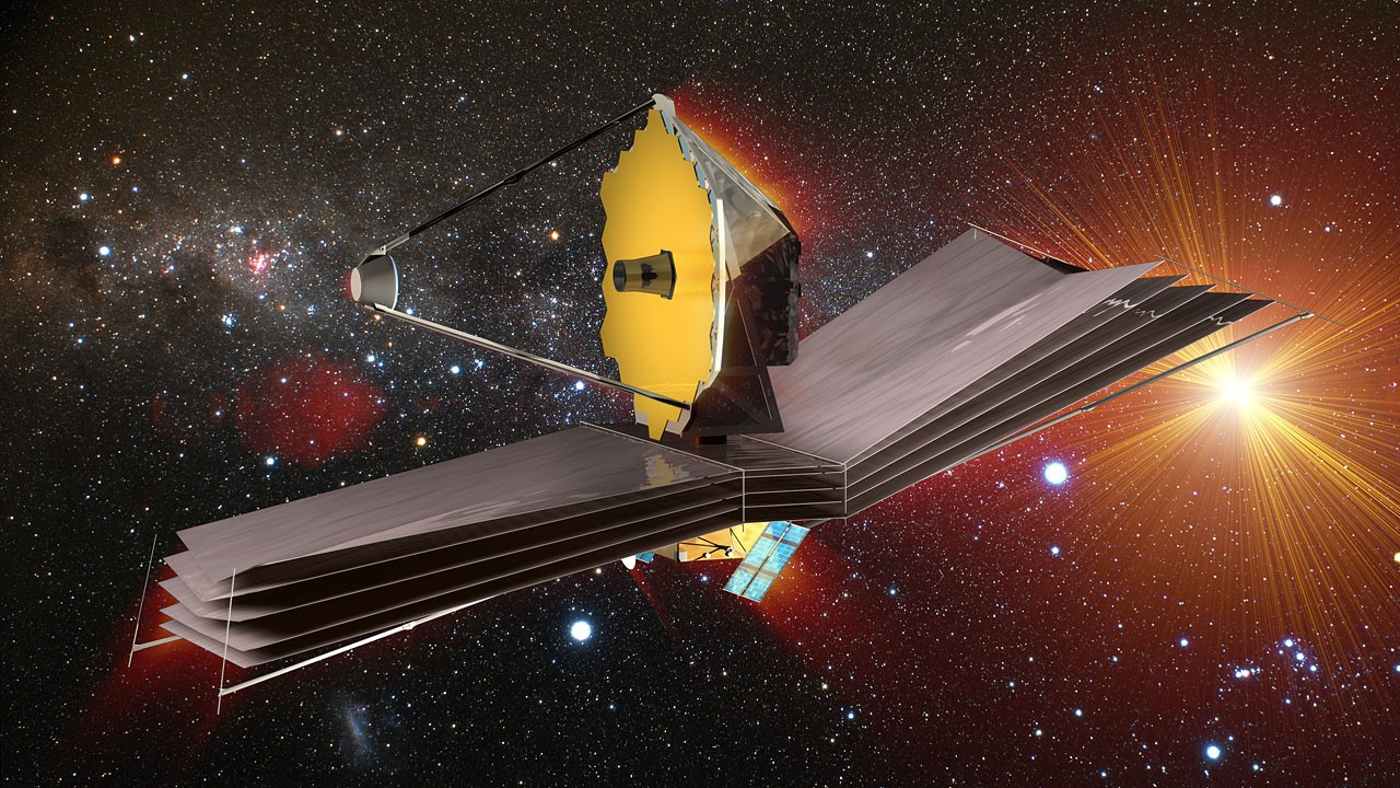
One recurring issue that NASA has faced is delays and budget increases on major missions such as:
-
The James Webb Space Telescope
-
The Roman Space Telescope
-
Mars Sample Return
-
Artemis lander development
The acting chief said that while these missions are scientifically groundbreaking, the agency must improve how they are managed. The shakeups will therefore focus on strengthening oversight and reducing the risk of cost overruns.
New procedures will include:
-
More frequent progress audits
-
Independent review boards
-
Revised budgeting techniques
-
Early risk identification
-
Greater transparency between centers and contractors
NASA’s leadership wants to ensure that complex missions proceed with fewer surprises and clearer timelines.
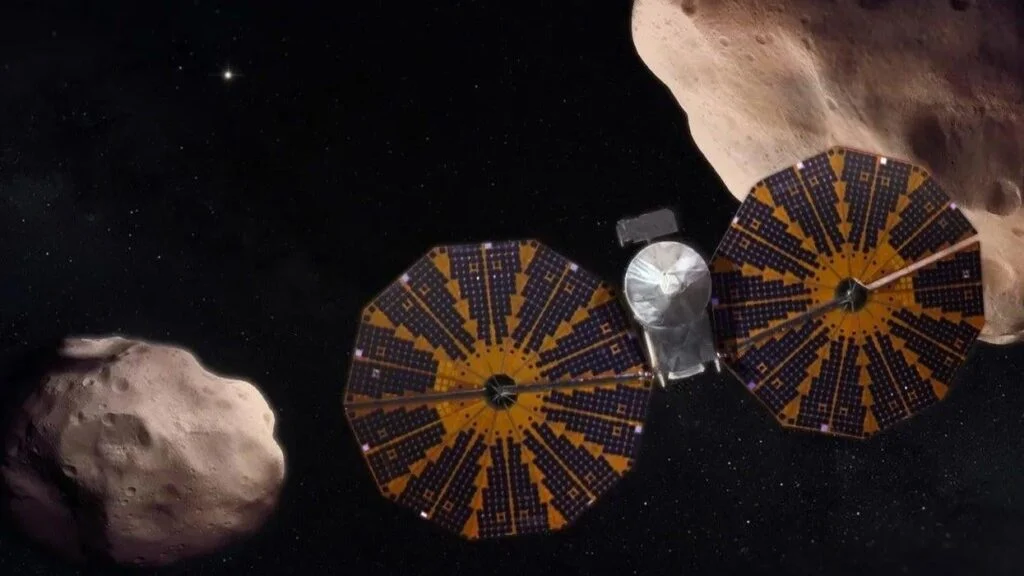
Mars Sample Return: A Special Case Study
The acting administrator specifically mentioned Mars Sample Return, calling it one of NASA’s most challenging and expensive missions. MSR has sparked debate within the scientific community and U.S. government because of its escalating costs and extended timeline.
In response, the shakeups will include:
-
A restructured MSR program office
-
Tighter integration between NASA and the European Space Agency
-
New design review cycles
-
More realistic cost and schedule forecasts
The mission is still considered essential, but it needs a more streamlined approach.
Adapting to Global Competition
The acting NASA chief made it clear that global competition is a major reason behind the shakeups. China, in particular, has made rapid progress in:
-
Lunar exploration
-
Space station construction
-
Sample return missions
-
Deep-space probes
If NASA does not accelerate its progress, the U.S. risks falling behind in key areas of space science and exploration.
The shakeups are part of a broader strategy to ensure that NASA remains a leader on:
-
The Moon
-
Mars
-
Deep space missions
-
Planetary science
-
Space technology innovation
International collaboration remains important, but NASA wants to ensure the U.S. maintains a competitive edge.
Public Communication and Transparency
The acting chief also emphasized better communication with the public. NASA is one of the most admired government agencies, but many of its internal processes remain behind the scenes. The leadership believes greater transparency will build trust, maintain political support, and encourage future generations of scientists and engineers.
The shakeups include:
-
More open briefings
-
Improved public updates
-
Clearer explanations of mission delays or changes
-
Stronger engagement with students and educators
NASA understands that public excitement plays a crucial role in securing future funding.
What This Means for NASA’s Future
The shakeups represent a strategic shift toward a more modern, agile, and competitive NASA. The changes are not just structural—they reflect a new philosophy of leadership.
NASA’s future under these reforms may include:
-
Faster mission development
-
More affordable spacecraft
-
Closer coordination with industry
-
Improved reliability in schedules
-
Stronger scientific output
-
A more dynamic, younger workforce
Most importantly, NASA will be better equipped to deliver ambitious missions such as:
-
Artemis crewed landings
-
A sustained human presence on the Moon
-
Mars Sample Return
-
Crewed missions to Mars in the future
-
New observatories that look deeper into the universe
Conclusion
The acting NASA chief’s announcement of further “shakeups” marks a decisive moment for America’s space agency. As NASA prepares for historic missions and faces increasing global competition, these structural reforms are not only timely—they are essential. By reshaping its internal organization, strengthening commercial partnerships, improving mission management, and investing in workforce development, NASA is positioning itself for a stronger and more ambitious future.
The shakeups are designed to make NASA more innovative, more efficient, and more prepared for the challenges of 21st-century space exploration. With these changes, the agency is sending a clear message: NASA is not standing still. It is evolving, accelerating, and ready to lead humanity into the next great chapter of discovery.
Read Also: Keep your face towards the sunshine and shadows will fall behind you
Watch Also: https://www.youtube.com/@TravelsofTheWorld24











Leave a Reply