Space is full of surprises, and scientists may have found a planet similar in size to Earth. This exciting discovery has many people talking because finding another planet like ours is rare. But there’s a catch: the planet may not be exactly like Earth in the way we usually think.
The planet was spotted using advanced telescopes and space observation tools, and researchers are carefully studying its features. While its size is similar to Earth, scientists warn that other factors, like temperature, atmosphere, and distance from its star, make it very different from our home planet.
How Scientists Found the Planet
The new planet was discovered using methods that detect tiny changes in a star’s light. When a planet passes in front of its star, it blocks a little bit of light. This method is called the transit method.
Using this method, astronomers noticed regular dips in the star’s brightness, which suggested a planet was orbiting it. By measuring these dips, they could estimate the planet’s size, orbit, and distance from the star.
Why Size Matters
The new planet is called Earth-sized because its diameter is close to that of Earth. Size is important because:
-
Smaller planets may be rocky like Earth
-
Larger planets may be gas giants like Jupiter
-
Earth-sized planets are more likely to have conditions for life
Being Earth-sized does not mean it is Earth-like in every way, but it is an important clue for scientists searching for habitable planets.
The Catch: Conditions May Not Be Right
Here’s the tricky part: the planet may not have conditions suitable for life.
Some possible challenges:
-
It may be too close or too far from its star, making it too hot or too cold
-
It may lack an atmosphere to support water or air
-
Its surface may be hostile, with high radiation or extreme weather
So while the planet’s size is similar to Earth, it may be very different in terms of habitability.
Why Scientists Are Excited
Even with the catch, this discovery is exciting because:
-
It adds to the growing list of Earth-sized planets in the galaxy
-
It helps scientists understand how planets form and evolve
-
It gives clues about where life could exist in the universe
Finding planets of similar size is rare and valuable, even if they are not exactly like Earth.
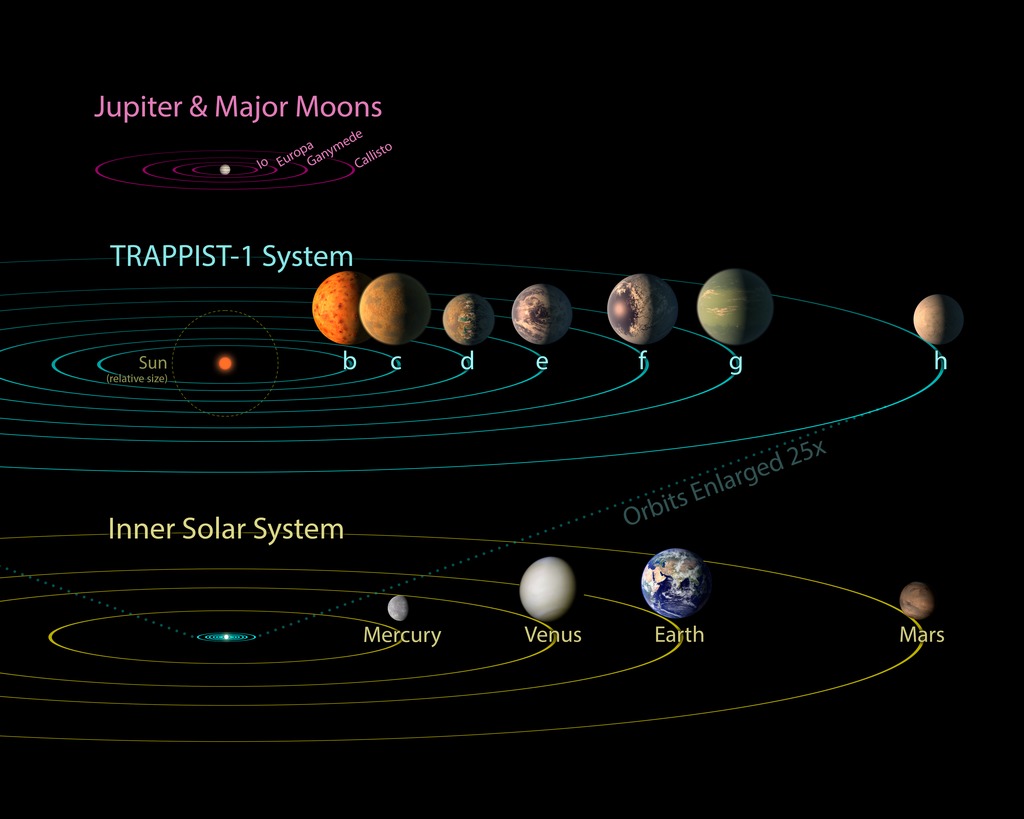
How Far Away Is the Planet?
The planet is located many light-years away, meaning its light takes years to reach Earth. A light-year is the distance light travels in a year—about 9.5 trillion kilometers.
This means that even though we discovered it, we cannot travel there anytime soon. Scientists study these distant planets with telescopes and computers to understand them better.
What Makes a Planet “Earth-Like”?
Being Earth-like is more than size. Scientists look for:
-
Distance from its star (habitable zone)
-
Presence of water
-
Atmosphere
-
Temperature and climate
-
Chemical composition
This new planet may be Earth-sized, but it may fail some of these tests, which is why scientists call it “not fully Earth-like.”
How Scientists Study These Planets
Scientists cannot visit these planets yet, so they rely on:
-
Telescopes that measure light
-
Spectroscopy to study chemical composition
-
Computer models to simulate atmospheres and climates
These methods help estimate whether a planet could support life or what it might be like on the surface.
Could Life Exist There?
Life as we know it depends on water, energy, and the right temperature. This planet may:
-
Be too hot or too cold for life
-
Lack water or have extreme weather conditions
-
Have a star that emits harmful radiation
While it is exciting to find Earth-sized planets, scientists are careful to say “it may not be habitable.”
Why This Discovery Matters
Finding an Earth-sized planet is a step forward in understanding our galaxy. It shows that:
-
Planets like ours exist elsewhere
-
The universe is full of diverse worlds
-
Searching for habitable planets is possible with current technology
Even planets that are not perfect for life help scientists learn more about planet formation and evolution.
The Role of Space Telescopes
Space telescopes like Kepler, TESS, and Hubble help discover planets. They are equipped to:
-
Detect small dips in starlight
-
Observe planets at different distances
-
Study atmospheres and chemical composition
Future telescopes will improve our ability to find more Earth-like planets.
What’s Next for This Planet
Scientists plan to:
-
Observe it more carefully
-
Check its orbit and size measurements
-
Look for signs of an atmosphere
-
Compare it with other Earth-sized planets
Each new observation gives more insight into whether it could support life or has interesting features.
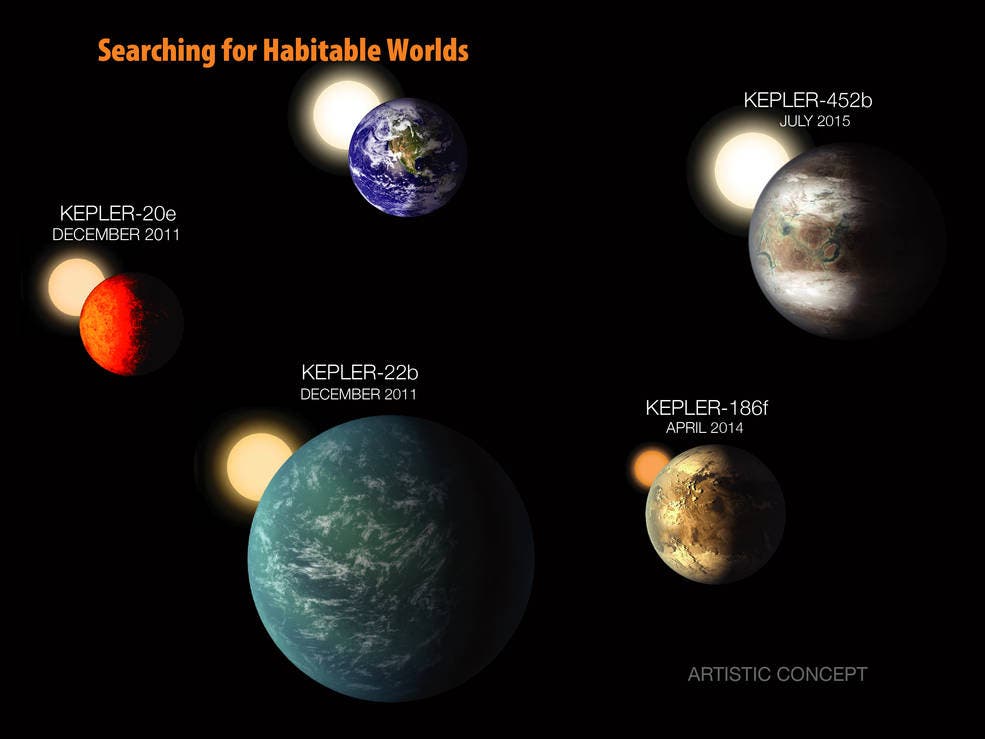
How Many Earth-Sized Planets Are Known?
There are now hundreds of Earth-sized planets discovered in the Milky Way. Some are:
-
Too hot or too cold
-
Orbiting stars very different from the Sun
-
In binary star systems
The discovery of this planet adds to the growing catalog and helps scientists identify which planets are worth studying further.
The Importance of the Habitable Zone
The “habitable zone” is the area around a star where liquid water could exist. A planet’s position in this zone is crucial for life.
This new planet may or may not be in the habitable zone. That’s the catch—it is Earth-sized, but it may not have the right temperature or conditions for life.
How Technology Helps
Modern technology allows astronomers to study planets billions of kilometers away. Tools include:
-
High-resolution telescopes
-
Light spectrum analysis
-
Computer simulations
-
Data from multiple observatories
These technologies help scientists estimate atmosphere, climate, and surface conditions without visiting the planet.
Why Size Alone Is Not Enough
Many people get excited when a planet is called Earth-sized. But size is only one factor:
-
A bigger planet may have too much gravity for humans
-
A smaller planet may have weak gravity and poor atmosphere
-
Other factors like star type and distance determine habitability
So while size is important, scientists need more data to judge if it could support life.
Could Humans Visit This Planet?
Not anytime soon. The planet is light-years away, making travel impossible with current technology.
For now, scientists focus on:
-
Observing it remotely
-
Learning about its composition and orbit
-
Comparing it to other planets in our galaxy
Even without visiting, studying these planets teaches us about the universe and our place in it.
Public Excitement
News about Earth-sized planets captures public attention because:
-
People dream of finding another Earth
-
It raises questions about life elsewhere
-
Space discoveries inspire future scientists and explorers
However, scientists emphasize caution: not every Earth-sized planet is habitable.
The Next Steps in Planet Research
Astronomers will continue to:
-
Use more powerful telescopes
-
Study atmospheres and chemical makeup
-
Search for signs of water or life
-
Compare with other planets around similar stars
Each discovery improves our understanding of the universe and helps focus future searches for habitable worlds.
Final Thoughts
The discovery of a new Earth-sized planet is exciting, but the “catch” reminds us that size alone does not mean it is Earth-like. Scientists must consider temperature, atmosphere, distance from its star, and other conditions.
Even if it cannot support life, this planet teaches us:
-
The universe is full of diverse worlds
-
Humans are learning more about planets every year
-
Technology allows us to study distant planets in detail
Finding Earth-sized planets is just the first step. The next steps will tell us which of these worlds could truly be a “new Earth.”
Exploring space is a journey of curiosity, patience, and discovery. Each new planet brings us closer to understanding how rare or common Earth-like worlds really are.
Read Also: Keep your face towards the sunshine and shadows will fall behind you
Watch Also: https://www.youtube.com/@TravelsofTheWorld24











Leave a Reply