This week, groundbreaking research and discoveries have captured the attention of scientists and enthusiasts around the world. From the deep Earth to the age of dinosaurs, recent findings are shedding light on our planet’s hidden mysteries and its long evolutionary history. Key highlights include evidence that Earth’s inner core may be spinning slower than the surface, the discovery of rare dinosaur nests in India’s Narmada Valley, and several other significant developments in astronomy, biology, and environmental science.
Here is a comprehensive overview of the most compelling science news of the week.
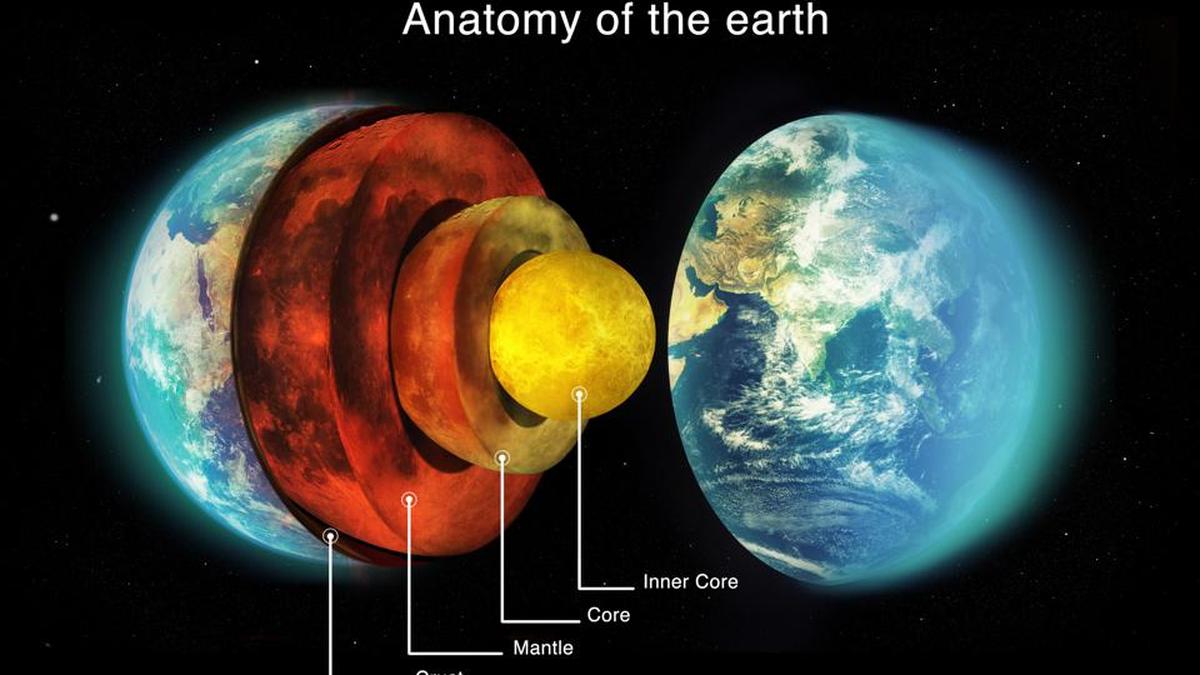
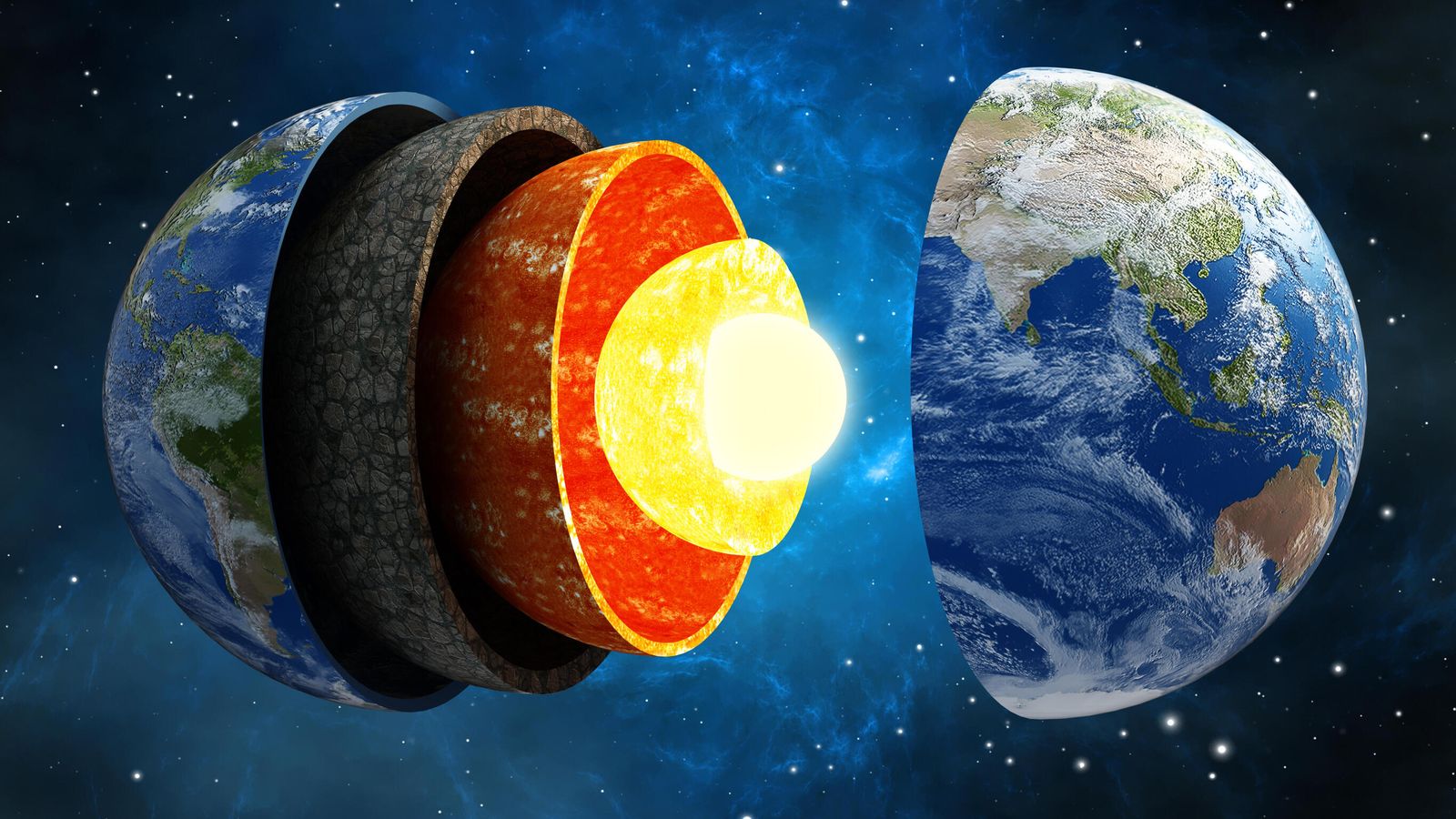
Earth’s Inner Core Spinning Slower Than the Surface
Recent seismological studies suggest that Earth’s inner core—the solid iron-nickel sphere at the planet’s center—may be rotating slower than the crust and mantle. This discovery is part of ongoing research into the long-debated dynamics of the inner core, which plays a crucial role in generating Earth’s magnetic field through the geodynamo process.
Key Findings
-
Seismic Wave Analysis: By examining the travel times of seismic waves from earthquakes over the past several decades, scientists identified subtle anomalies suggesting the inner core’s rotation may lag behind the surface.
-
Seven-Decade Cycle: Evidence points to a periodic cycle, roughly 70 years long, during which the inner core alternates between super-rotation (faster than the surface) and sub-rotation (slower than the surface).
-
Implications for Geophysics: Changes in inner core rotation affect the geomagnetic field, potentially contributing to fluctuations in magnetic pole locations and variations in field strength.
Understanding these dynamics not only provides insight into Earth’s magnetic shield but also informs models of planetary interiors and the behavior of other celestial bodies with metallic cores.
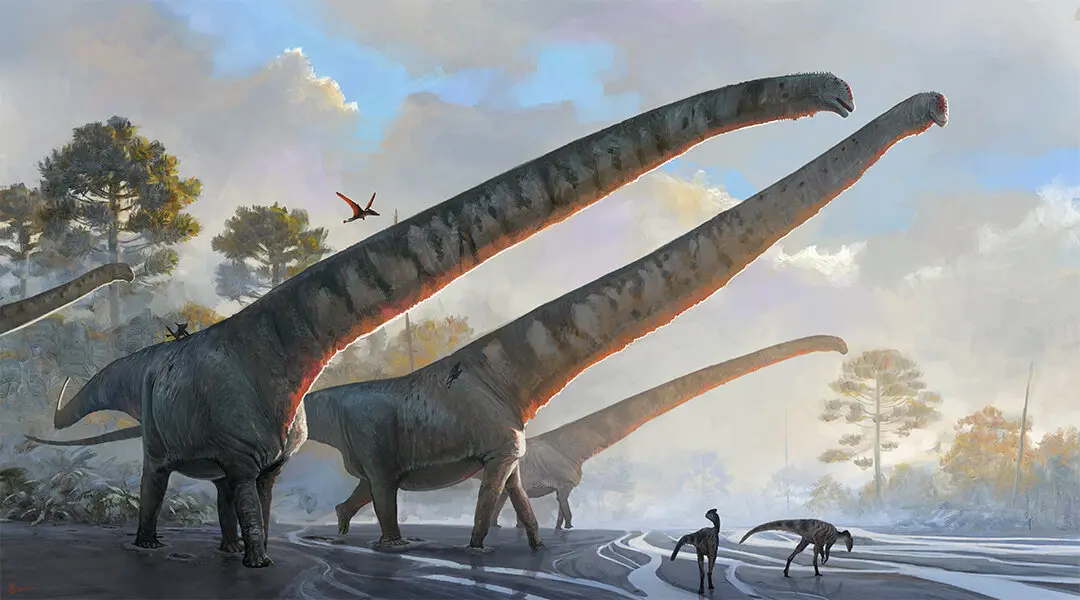
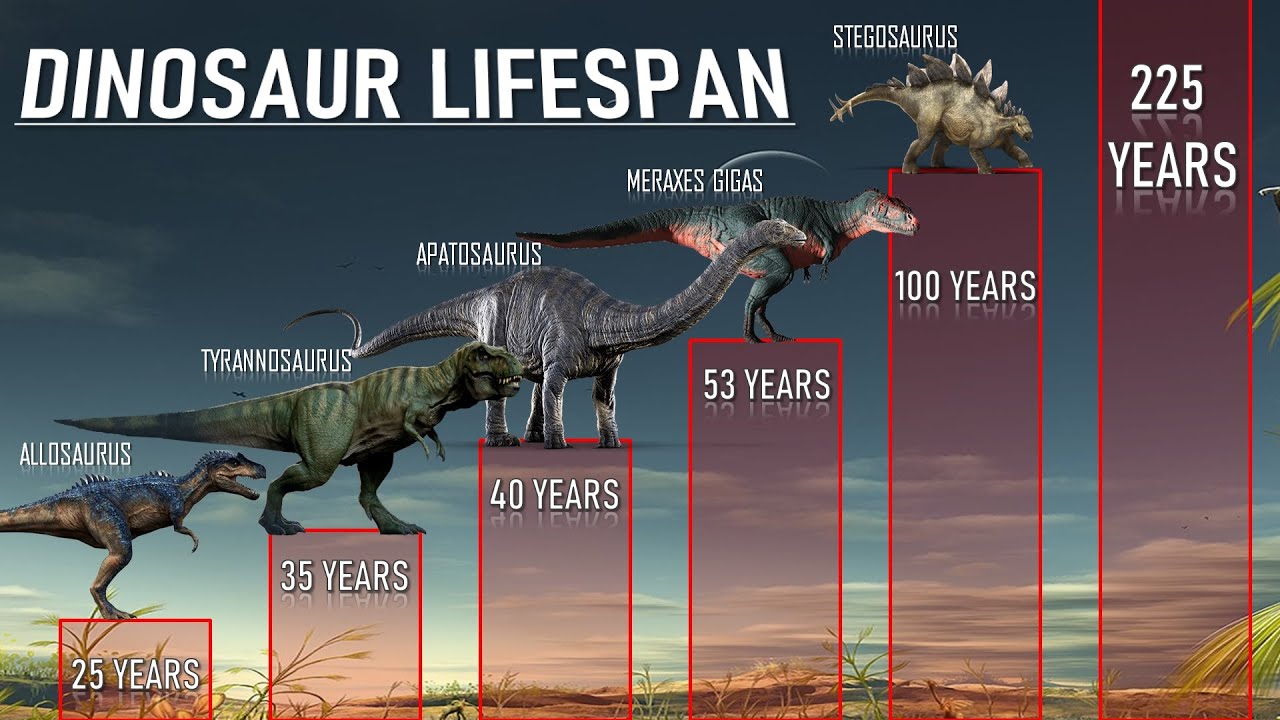
Rare Dinosaur Nests Discovered in Narmada Valley, India
Paleontologists have unearthed previously unknown dinosaur nests in India’s Narmada Valley, revealing remarkable insights into the behavior and reproductive strategies of prehistoric creatures. The discovery, dating back to the Late Cretaceous period, includes fossilized eggs and embryonic remains.
Highlights
-
Species Identification: The nests belong to rare theropod and sauropod species, some of which were previously undocumented in this region.
-
Egg Arrangement: Eggs were found in circular clusters, suggesting parental care and complex nesting behaviors.
-
Preservation: The fossils were exceptionally well-preserved due to sedimentation in river plains, allowing scientists to study embryonic development stages.
This discovery adds to the growing understanding of dinosaur reproductive biology and regional diversity during the Cretaceous. It also provides a rare glimpse into the nesting habits of species from a region that has long been underexplored paleontologically.
AI Boom and Environmental Impacts
The rapid expansion of artificial intelligence (AI) in 2025 continues to have environmental consequences, as highlighted in recent studies:
-
CO2 Emissions: Training large AI models has contributed to significant increases in carbon emissions due to high electricity consumption in data centers.
-
Water Usage: Cooling high-performance computing systems consumes millions of liters of water daily, particularly in regions hosting AI clusters.
-
Energy Demand: Global AI operations now rival the electricity consumption of mid-sized countries, raising concerns about sustainability.
Scientists and policymakers are calling for greener AI technologies, including renewable-powered data centers, energy-efficient hardware, and optimized algorithms to reduce the environmental footprint of AI.
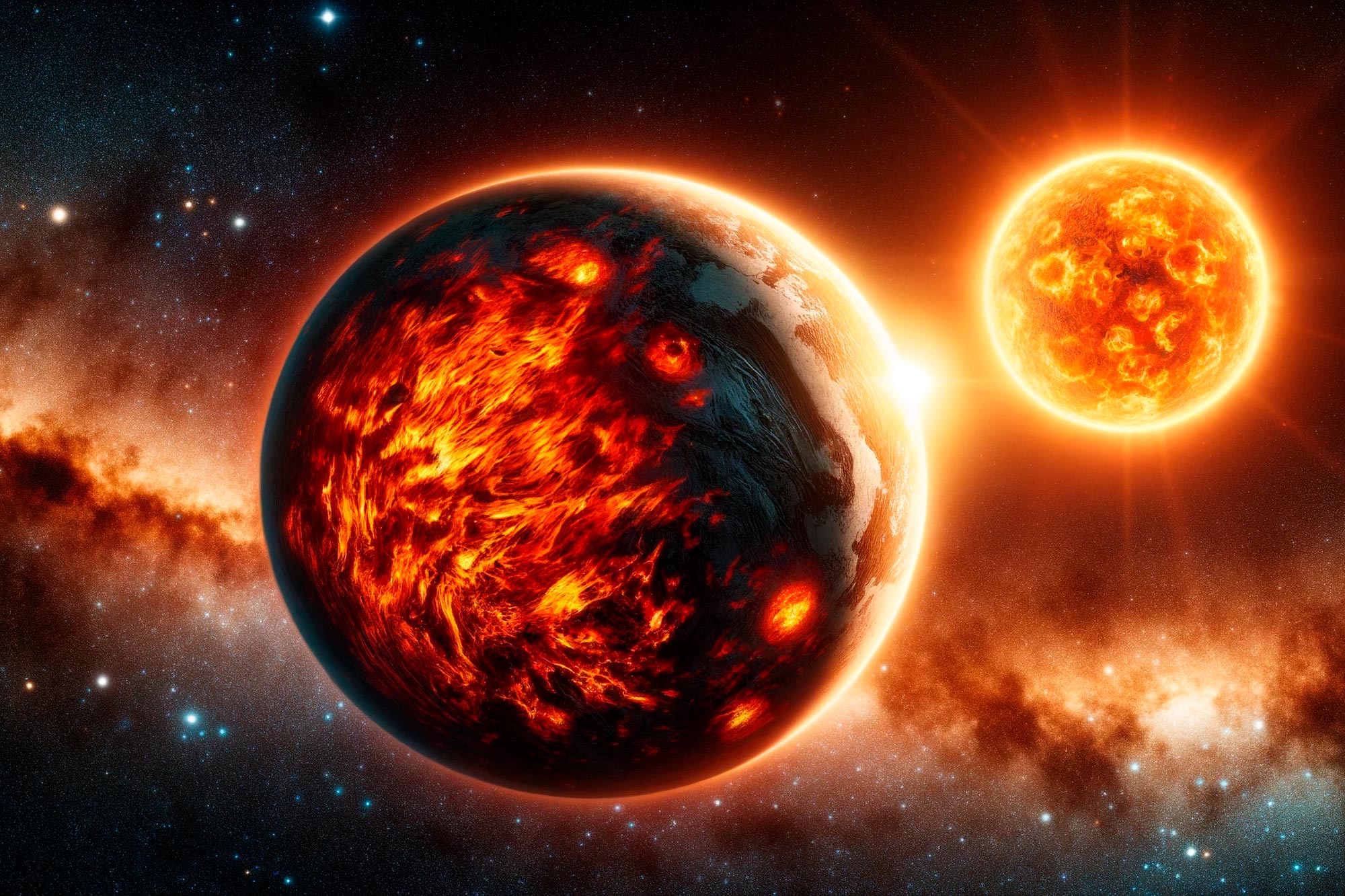
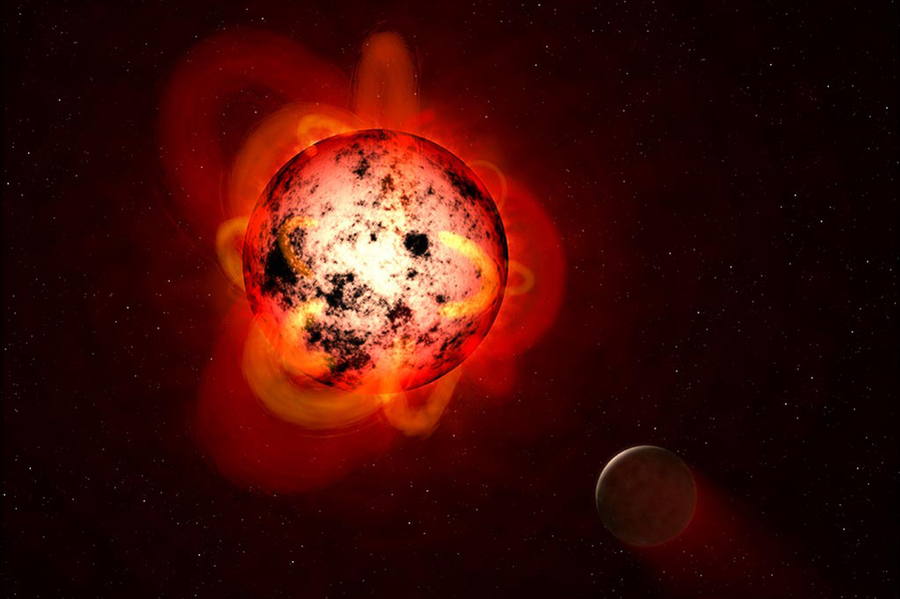
Exoplanet Discoveries Continue to Fascinate
Astronomers have reported several notable exoplanet findings this week:
-
Earth-Sized Lava Hemisphere Planet: A planet, TOI-2339b, with a molten dayside and a 4.2-day orbital period, demonstrates the extreme diversity of terrestrial exoplanets.
-
Planet-Induced Stellar Spin-Up: Studies reveal that massive close-in planets can influence the rotation and magnetic activity of their host stars, effectively keeping stars “young.”
-
Potential Biosignatures Detected: Atmospheric analysis of planets like Kepler-442c shows chemical signals that could hint at biological activity, reigniting the search for extraterrestrial life.
These discoveries expand our understanding of planetary formation, tidal interactions, and the potential habitability of worlds beyond our solar system.
Advances in Human Health and Nutrition
Medical researchers have unveiled findings that could impact public health:
-
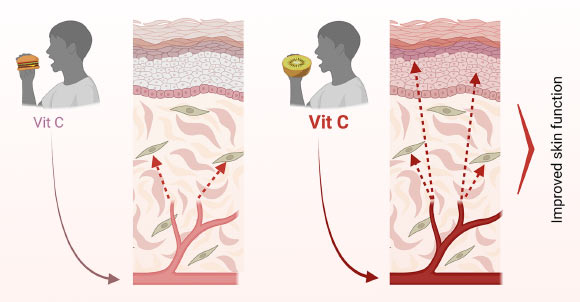
Vitamin C and Skin Renewal: Studies confirm that collagen production and skin regeneration directly respond to vitamin C intake, highlighting the importance of diet in skin health.
-
Kissing Evolution: Anthropologists report that kissing behavior may have evolved in common ancestors of humans and large apes over 21 million years ago, revealing insights into social bonding and communication.
-
Collagen Research: Insights into how nutrition influences tissue regeneration have implications for aging, wound healing, and regenerative medicine.
These discoveries emphasize the interplay between biology, evolution, and human health, offering practical takeaways for lifestyle and medical science.
Read Also: Keep your face towards the sunshine and shadows will fall behind you
Environmental and Marine Science Insights
-
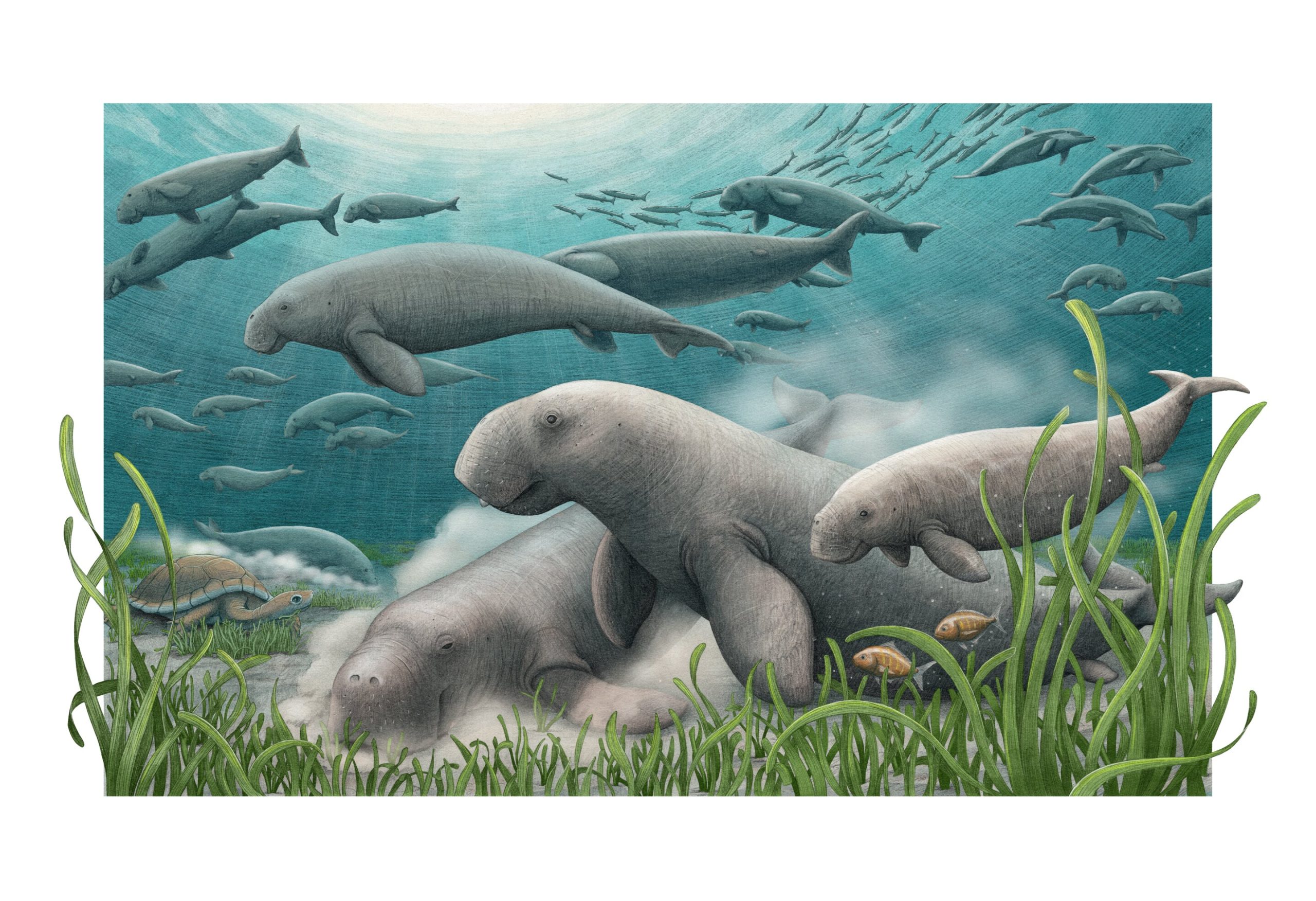
Sea Cow Communities Shape Seagrass Ecosystems: Marine biologists found that sea cows (dugongs) have been engineering Arabian Gulf seagrass ecosystems for over 20 million years, demonstrating the long-term ecological impact of megafauna.
-
Climate Monitoring: New data from global environmental monitoring systems reveal that climate-related events are intensifying, emphasizing the urgent need for sustainable energy and conservation efforts.
-
Sustainable Technology Development: Integration of AI in environmental monitoring allows for more precise tracking of CO2 levels, water quality, and biodiversity, highlighting the role of technology in sustainability.
These studies underscore the importance of long-term ecological research and human impact on planetary systems.
Read Also: Keep your face towards the sunshine and shadows will fall behind you
Fossil Discoveries Illuminate Evolutionary History
In addition to dinosaur nests, other fossil findings this week have provided insights into evolution:
-
Homo erectus Fossil: A 1.5-million-year-old fossil reveals new details about the morphology and behavior of early humans, including possible tool use and dietary adaptations.
-
Primate Behavior: Fossil evidence suggests that some social behaviors, such as bonding and grooming, may have evolved tens of millions of years ago, offering clues about the origins of modern social structures.
-
Marine Life Evolution: Discoveries of ancient sea creatures continue to inform our understanding of ecosystems and evolutionary patterns over geological timescales.
Fossils remain a critical window into Earth’s past, allowing scientists to reconstruct the life, climate, and environment of ancient eras.
Technology and Space Research Highlights
-
AI in Astronomy: Machine learning algorithms are helping astronomers analyze vast datasets, accelerating the discovery of exoplanets and cosmic anomalies.
-
Quantum Computing Applications: Quantum simulations are being used to model planetary cores and extreme physical conditions, offering insights into both geophysics and astrophysics.
-
Satellite Observations: High-resolution satellites continue to provide real-time monitoring of environmental changes, ice melt, and ocean dynamics.
These technological advancements illustrate how interdisciplinary approaches are enhancing scientific understanding across multiple fields.
Key Takeaways from This Week’s Science
-
Dynamic Earth: Evidence of the inner core’s variable rotation and its impact on magnetic fields emphasizes the complexity of Earth’s interior.
-
Paleontological Riches: New dinosaur nests and ancient fossils in India expand knowledge of prehistoric life and behavior.
-
AI and Sustainability: The environmental footprint of AI underscores the urgent need for eco-friendly technological solutions.
-
Exoplanet Diversity: Discoveries of lava worlds, tidal interactions, and potential biosignatures highlight the variety and complexity of planets beyond our solar system.
-
Human Health Insights: Evolutionary and nutritional research continues to reveal the connections between behavior, biology, and well-being.
Together, these discoveries reflect the ever-expanding frontiers of science, from the depths of Earth to the far reaches of the cosmos.
Conclusion: Connecting Past, Present, and Future
This week’s scientific developments illustrate the intricate connections between Earth’s interior, ancient life, technological advancement, and our understanding of the universe. From observing the subtle slowing of Earth’s inner core to unearthing dinosaur nests in Narmada Valley, scientists are piecing together the story of our planet and the life it supports.
Simultaneously, the environmental impact of AI reminds us that technological progress must be balanced with sustainability, while discoveries in astronomy and health highlight the ongoing quest to understand our place in the cosmos. These findings collectively underscore the importance of interdisciplinary research and the need for thoughtful stewardship of our planet and its resources.
As researchers continue to explore the unknown, the coming months and years promise even more transformative discoveries, bridging the ancient past with the rapidly evolving present and shaping the future of science and human knowledge.
Watch Also: https://www.youtube.com/@TravelsofTheWorld24











Leave a Reply