Scientific research continues to expand as our understanding of Earth grows more complex. One of the most significant developments in the field of geosciences is the introduction of a new dedicated section, Solid Earth Geophysics, in the reputable journal Frontiers in Earth Science. This addition marks a major milestone for researchers, educators, and students who study the physical structure, processes, and dynamic behavior of the solid Earth. The new section not only strengthens the scientific scope of the journal but also creates a specialized platform to explore one of the most critical branches of geoscience.
Understanding Solid Earth Geophysics
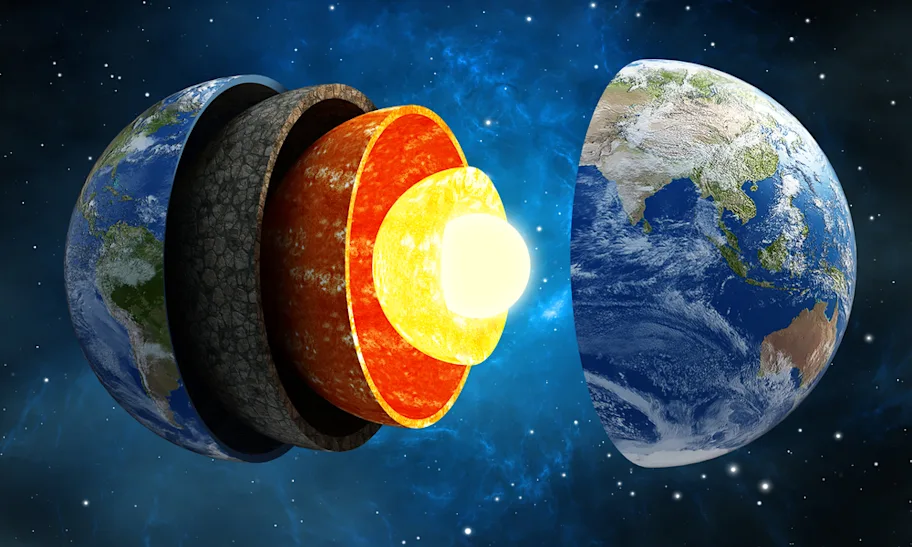
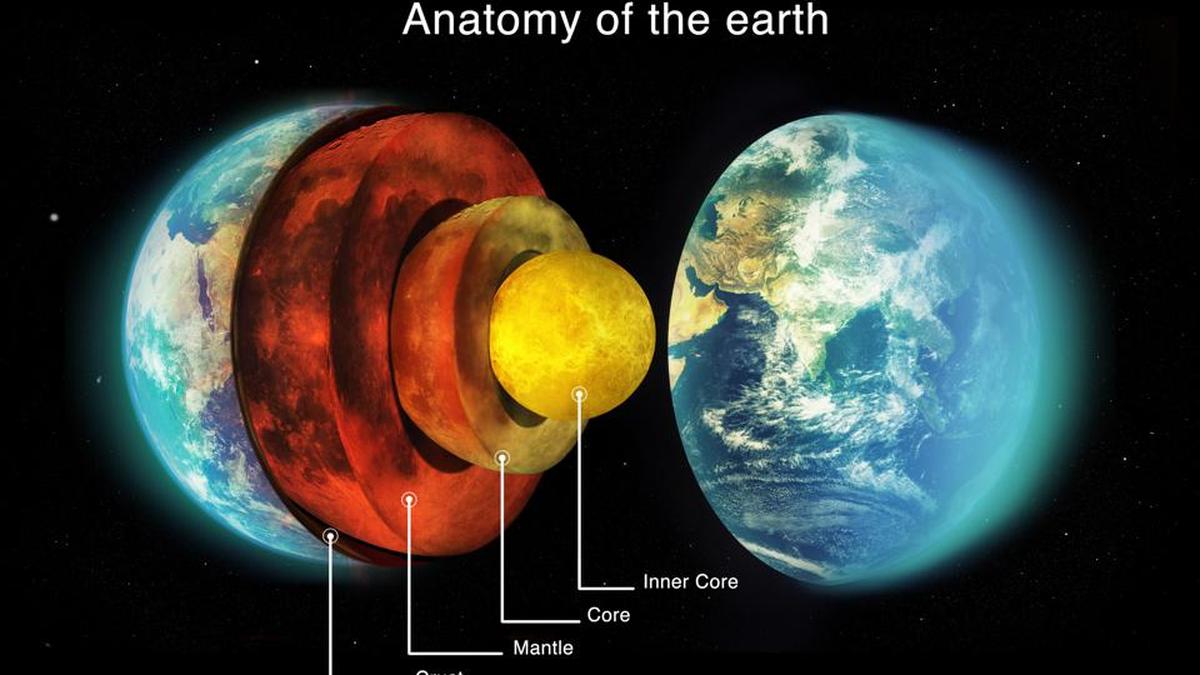
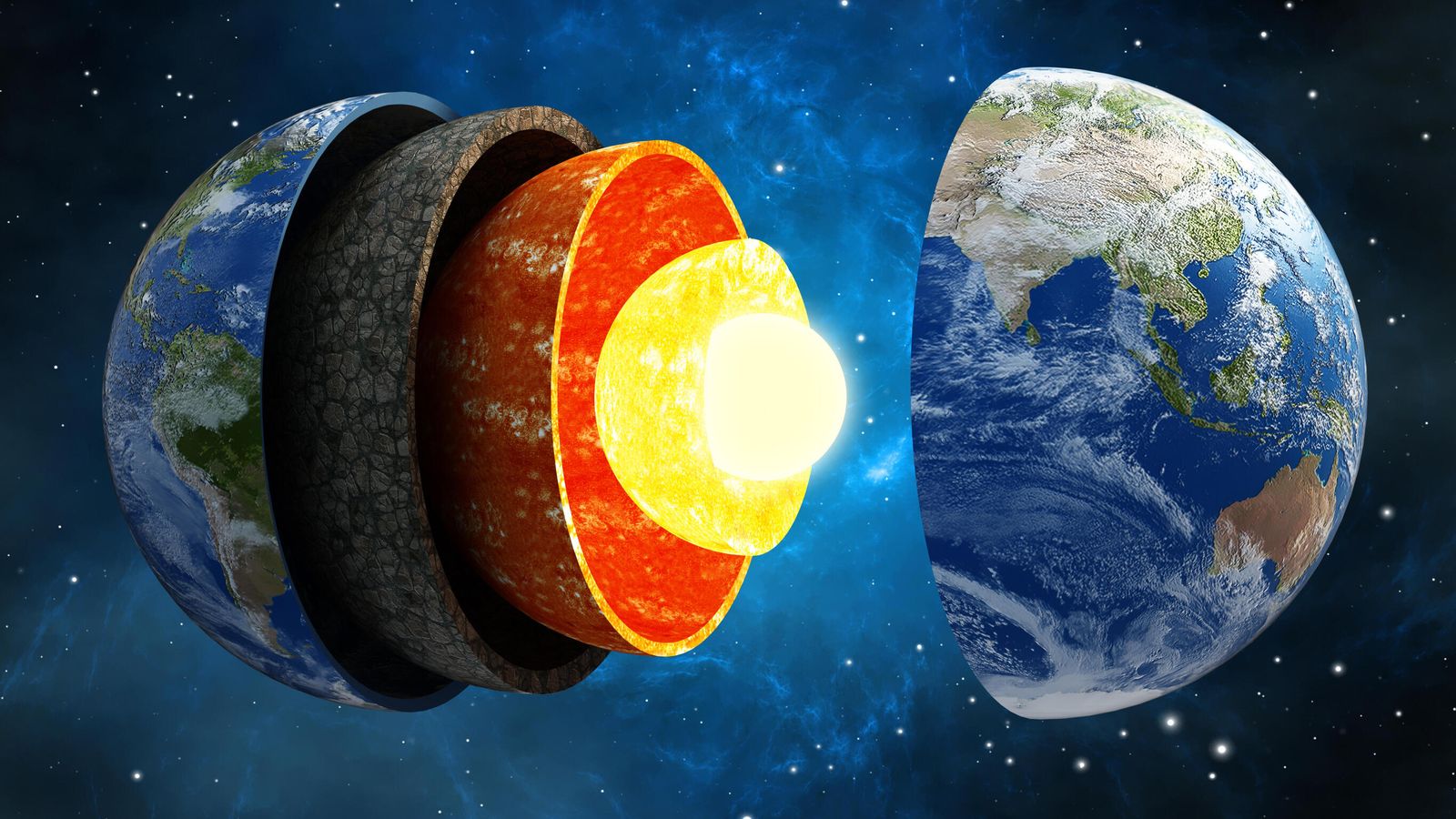
Solid Earth geophysics focuses on the study of the Earth’s solid components—its crust, mantle, and core—and the physical processes that shape the planet. This includes earthquakes, volcanic activity, plate tectonics, mountain building, geothermal energy, and the formation of natural resources. Scientists use advanced methods such as seismology, geomagnetism, gravimetry, and geodesy to investigate Earth’s interior and its long-term evolution.
The goal of solid Earth geophysics is not only to understand the structure of the Earth but also to explain how it changes over time and how those changes impact human life. For instance, understanding seismic activity helps improve earthquake preparedness, while studying the thermal structure of the Earth assists in geothermal resource exploration. Thus, solid Earth geophysics plays a vital role in disaster management, resource discovery, and sustainable development.
Why a New Section Was Needed
Before the introduction of the Solid Earth Geophysics section, research in this area was often scattered across various sections of Frontiers in Earth Science, such as Geophysics, Volcanology, or Structural Geology. As the field grew rapidly, the need for a dedicated home for research became obvious. The new section addresses several important academic and scientific needs:
1. Increasing Research Output
Advances in remote sensing, computational geoscience, and field instrumentation have led to a significant rise in the number of studies examining Earth’s interior. A separate section provides space to accommodate this growing body of work.
2. Encouraging Specialized Collaboration
By creating a distinct category, the journal encourages collaboration among specialists who investigate similar topics. Researchers can now more easily find relevant publications, connect with peers, and contribute to collective scientific progress.
3. Promoting Interdisciplinary Work
Solid Earth geophysics overlaps with engineering, environmental science, planetary science, and data science. A focused section helps make these interdisciplinary links clearer while maintaining scientific coherence.
4. Enhancing Visibility for Geophysics Research
Dedicated sections increase the visibility of specific fields. For scientists working on Earth’s interior, this new section ensures that their research receives focused attention.
Scope of the Solid Earth Geophysics Section
The new section is designed to cover a wide range of topics, making it a comprehensive home for solid Earth research. Key areas include:
• Seismology
This includes the study of earthquakes, seismic waves, and Earth’s internal layering. Seismology provides essential data about Earth’s composition and helps improve risk assessments for earthquake-prone zones.
• Geodynamics
Geodynamics examines the large-scale movement and deformation of Earth, including mantle convection, plate tectonics, and lithospheric evolution. This research is crucial for understanding continental drift, mountain building, and volcanic activity.
• Geomagnetism and Paleomagnetism
These fields explore the Earth’s magnetic field, both past and present. Studies help reconstruct continental movements and explain phenomena such as magnetic pole reversals.
• Gravity and Geodesy
Gravity measurements reveal density variations inside the Earth. Geodesy, meanwhile, focuses on precise measurements of Earth’s shape, rotation, and gravitational field.
• Volcanology (Solid Earth Perspective)
While volcanology has its own field, solid Earth geophysics provides the physical and mathematical foundation for understanding magma movement, eruption mechanisms, and volcanic hazards.
• Tectonophysics
This includes research on stress, strain, and the mechanical behavior of Earth’s crust and mantle. It helps in modeling fault systems and understanding earthquake cycles.
• Geophysical Imaging
Using seismic tomography, electromagnetic surveys, and gravimetric imaging, scientists create 3D models of Earth’s interior. This contributes to mineral exploration, geothermal studies, and hazard assessments.
The Benefits for the Scientific Community
The new Solid Earth Geophysics section brings several benefits to researchers and the broader scientific world.
1. A Focused Peer-Review Environment
By assigning expert editors and reviewers from within the field, the section ensures rigorous, specialized, and constructive peer review. High-quality publications help raise the scientific standard and credibility of geophysical research.
2. A Centralized Knowledge Hub
Students, educators, and professionals now have a clear place to access the latest research in solid Earth geophysics. This creates a more efficient learning and teaching environment.
3. Faster Dissemination of Research
Open-access platforms like Frontiers help scientists share findings quickly. The dedicated section accelerates the publication pipeline by reducing overlap between different editorial domains.
4. Strengthening Global Collaboration
The new section welcomes contributions from all over the world, encouraging international collaboration on global geophysical challenges such as seismic hazards, volcanic risks, and resource sustainability.
Addressing Real-World Challenges
Solid Earth geophysics plays an important role in addressing some of humanity’s biggest challenges:
• Natural Disaster Mitigation
Seismology and tectonics research helps scientists map fault lines, assess earthquake probabilities, and improve early warning systems. Understanding volcanic activity also reduces risks to communities near active volcanoes.
• Resource Exploration
Advanced geophysical imaging allows for more accurate exploration of minerals, groundwater, hydrocarbons, and geothermal energy. This ensures more efficient resource use with reduced environmental impacts.
• Climate and Environmental Studies
Solid Earth processes influence long-term climate cycles through volcanic emissions, plate tectonics, and changes in Earth’s magnetic field. Studying these processes helps climate scientists develop more accurate models.
• Planetary Science
Many geophysical techniques used on Earth are also applied in planetary exploration. Understanding Earth’s interior helps scientists interpret data from Mars, the Moon, and other celestial bodies.
A Platform for Future Innovation
As the field continues to evolve, the Solid Earth Geophysics section is expected to become a hub for cutting-edge innovations:
-
AI-based geophysical modeling
-
Machine learning for earthquake prediction
-
High-resolution seismic tomography
-
Multidisciplinary tectonic simulations
-
Space-based geophysical observations
The journal’s commitment to open science will support transparent and accessible research, empowering the next generation of geoscientists.
Conclusion
The launch of the new Solid Earth Geophysics section in Frontiers in Earth Science represents a significant step forward for geoscience research. It acknowledges the rapid growth of solid Earth studies and provides a specialized platform for scientific discovery. With its broad scope, rigorous review process, and global accessibility, the section is set to advance our understanding of Earth’s interior, enhance natural disaster preparedness, and contribute to sustainable resource development. As research in geophysics expands, this new section will play a crucial role in shaping the future of Earth science.
Read Also: Keep your face towards the sunshine and shadows will fall behind you
Watch Also: https://www.youtube.com/@TravelsofTheWorld24










Leave a Reply